Getting Started
All workflows need a trigger to start. Once a workflow is triggered, it performs actions based on your setup.
Creating a Trigger
A trigger starts a workflow. The most common types are:
- Smartform Submit – Triggered when a form is submitted.
- Webhook – Triggered when an external system sends data.
- Cron Schedule – Triggered at a specific time or interval.
- Editor Submit – Triggered when an editor submits a document.
How to Set Up a Trigger:
- Open Workflow and click “Create New Workflow.”
- Select a trigger type (Smartform, Webhook, Cron, etc.).
- Configure the trigger settings.
- Click “Save” to finalize your trigger.
Adding Actions
Once a trigger is set, define what happens next by adding actions such as:
- Sending emails via Microsoft Outlook.
- Calling REST APIs to fetch or send data.
- Generating documents or PDFs.
- Sending messages through Kivra or Digipost.
How to Add an Action:
- Click ➕ inside your workflow.
- Select an action type (e.g., Send Email, API Call, Upload File).
- Configure the action settings.
- Save and repeat for additional actions.
Activating & Testing Your Workflow
Before a workflow can run, it must be activated.
How to Activate a Workflow:
- Open your workflow from the Workflow List.
- Click “Activate” (this will check for errors).
- If errors are found, correct them and try again.
How to Test Your Workflow:
- If your trigger is a Smartform, submit the form.
- If it’s a Webhook, send data to the webhook URL.
- If it’s a Cron Schedule, wait for the scheduled time.
Check the **workflow history ** to confirm the execution.
Example: Look Up Company Info via REST API
Imagine you have a Smartform where a user enters a company registration number. You can create a workflow that:
- Triggers when the field is updated.
- Calls a REST API to fetch company details.
- Fills in the company name and other data in the Smartform.
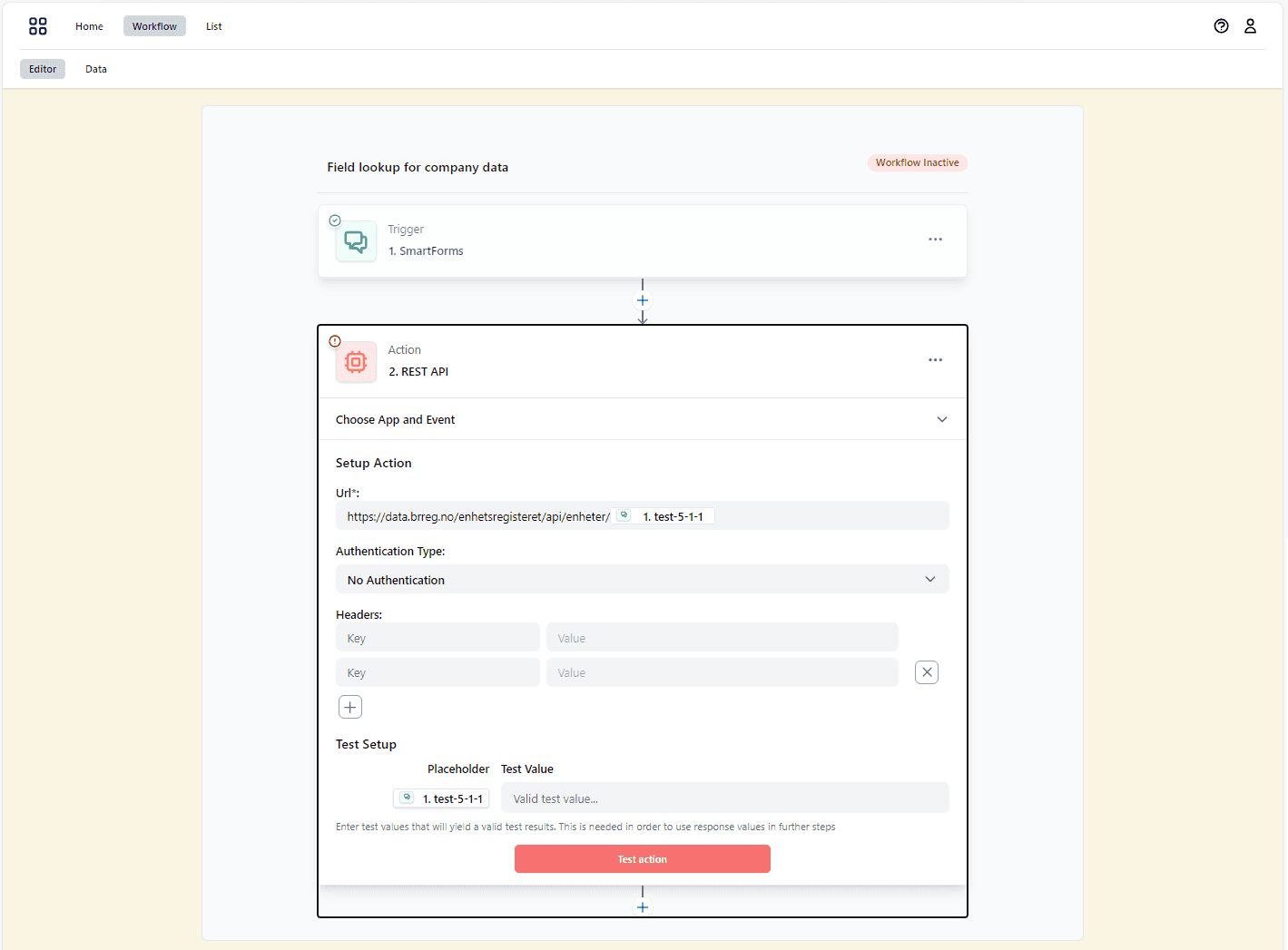
Example: looking up company information through a REST API when a special field changes and then filling data back into the Smartform.